Abstract
Introduction: There are four oral anti-Xa drugs currently available for clinical use in various indications. These drugs are claimed to mediate their therapeutic effects by solely targeting factor Xa. While these agents are structurally similar, their biochemical properties and their effects on blood coagulation differ. Such differences may impact their safety and efficacy profile. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the differences among factor Xa inhibitors in terms of their in vitro anticoagulant activity and other biochemical effects.
Materials and Methods: Commercially obtained powdered forms of Apixaban, Betrixaban, Edoxaban and Rivaroxaban were profiled in this study. Stock solutions of each drug were prepared at 1mg/ml. To investigate the effect on the whole blood clotting profile, thromboelastographic studies were carried out over a concentration range of 0.5 - 2.5 ug/ml and whole blood activated clotting time (ACT) was measured at 1.0 and 2.5 ug/ml. The anticoagulant profile in citrated human pool plasma was measured at concentrations of 0.062-1.0 ug/ml using such tests as prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). The anti-Xa effects of each agent were measured using a kinetic amydolytic method. The inhibitory potency was calculated in terms of IC-50. Thrombin generation inhibition studies on each drug were carried out in human pool plasma in a concentration range of 0.0-1.0 ug/ml using calibrated aotomated thrombogram (CAT) assay (Diagnostica Stago, Paris, France). Fibrinokinetics studies were carried out using an optical kinetic method, where thrombin was used to trigger clot formation. All results were compiled in terms of mean + 1 SD of 3-5 replicates.
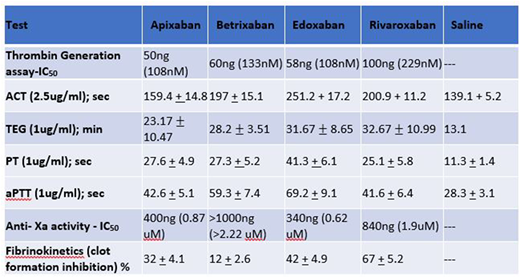
Results: All of the anti-Xa agents produced concentration and assay-dependent effects in these studies. The summary of each agent's effects at selected fixed concentrations and the IC-50 of the anti-Xa activity is given in the Table. In the whole blood ACT at 2.5ug/ml, Edoxaban showed the strongest anti-coagulant effects followed by Rivaroxaban > Betrixaban, whereas Apixaban showed minimal effects. In the TEG analysis at 1ug/ml, Edoxaban exhibited stronger anti-coagulant effects as measured by various TEG parameters, including R-time, K-time, alpha, and MA. Edoxaban and Rivaroxaban showed comparable effects followed by Betrixaban, whereas Apixaban exhibited weaker effects. In the PT assay at 1ug/ml, Edoxaban showed stronger effects, whereas Apixaban, Betrixaban and Rivaroxaban were comparable. aPTT at 1ug/ml revealed that Edoxaban was the strongest anti-Xa inhibitor followed by Betrixaban, whereas Apixaban and Rivaroxaban were comparable. In the anti-Xa assay Edoxaban was stronger (IC-50 = 340ng/ml, 0.62uM) than Apixaban (IC-50 =400ng, 0.87uM), Rivaroxaban (IC-50 = 840ng, 1.9uM) and Betrixaban (IC = >1000ng, >2.22 uM). In the thrombin generation assays at 1ug/ml, Apixaban showed the strongest inhibitory activity (IC-50 = 50ng/ml, 108nm) followed by Edoxaban (IC-50 = 58ng/ml, 108nm), Betrixaban (IC-50 = 60ngml, 133nm) while Rivaroxaban showed relatively weaker activity (IC-50 = 100ng/ml, 299nm). In the fibrinokinetics study at 1ug/ml, the anti-Xa agents produced varying degrees of inhibition with Rivaroxaban (67%), Edoxaban (42%), Apixaban (32%) and Betrixaban (12%).
Summary and Conclusion: These results demonstrate that the measured anti-Xa activity alone does not fully reflect the overall biologic spectrum of these agents. Assay dependent variations are exhibited by each of these drugs, revealing distinct individual profiles. Edoxaban was the only anti-Xa agent which consistently exhibited relatively stronger inhibitory profile which was proportional to its anti-Xa activity. These studies indicate that the oral anti-Xa drugs may modulate the hemostatic system through additional mechanisms independent of the inhibition of factor Xa.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal